Microsoft OAuth
Creating a custom Microsoft OAuth application
Step-by-step instructions below closely follow Microsoft documentation to create a new application for ngrok within the Azure portal.
Register an application
- Sign-in to the Azure portal then select or create a tenant for your application.
- Search for "Azure Active Directory" and select it.
- Select "App registrations" on the left hand navigation.
- Select "New registration" at the top.
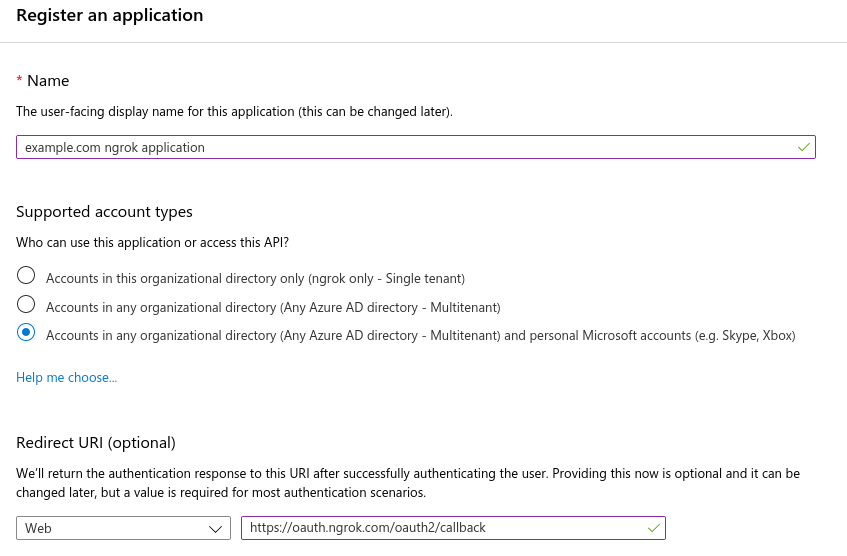
- Enter a name for your application.
- ngrok does not support single tenant applications. Choose supported account types from:
- Accounts in any organizational directory (Any Azure AD directory - Multitenant)
- Accounts in any organizational directory (Any Azure AD directory - Multitenant) and personal Microsoft accounts (e.g. Skype, Xbox)
- Choose a "Web" redirect URI and enter
https://idp.ngrok.com/oauth2/callback. - Register your application. The final form should resemble:
Configure your application
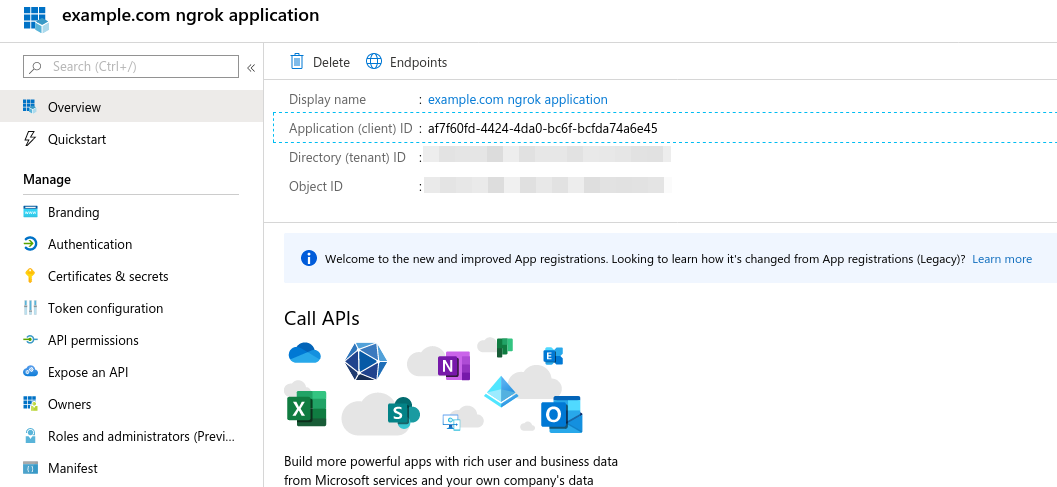
- When viewing your application, choose "Overview" on the left hand navigation.
- Store the "Application (client) ID" in the top information section for later.
- Select "API permissions" on the left hand navigation.
- Add additional scopes that your application requires and store them for later.
- Scopes which require an application review by Microsoft are unsupported.
- Scopes that require admin consent prevent tenants' users from authorizing until consent is granted.
- Ensure
User.Reador a more permissive scope (e.g.User.Read.All) is configured for ngrok. Example minimal configuration: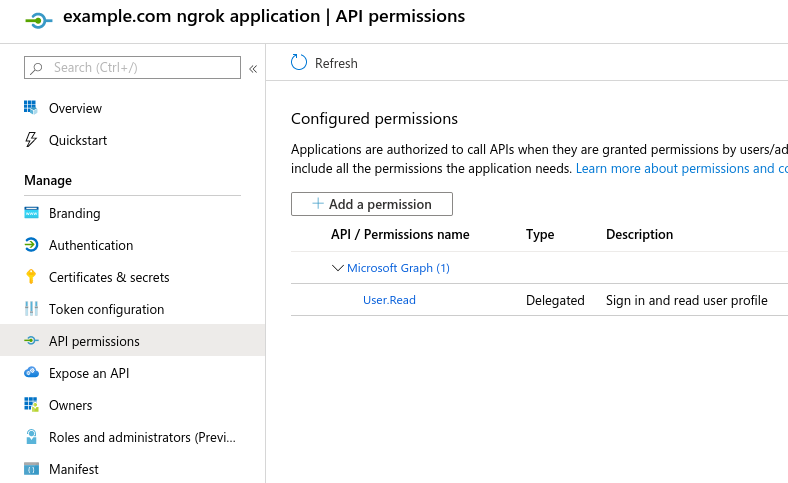
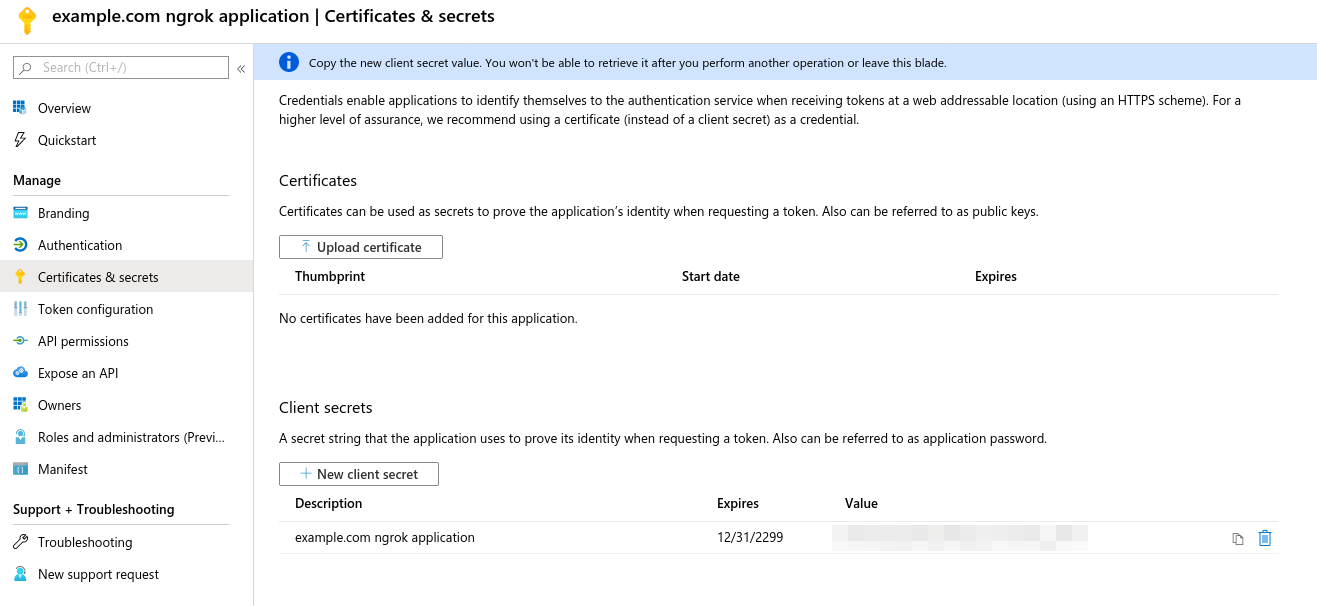
- Choose "Certificates and Secrets" on the left hand navigation.
- Select "New Client Secret" at the bottom, name the secret, set an expiration, and hit create.
- Creation is asynchronous. When complete, save the secret from the "Value" column (blurred below) for later:
Update your ngrok endpoint traffic policy
- Access the ngrok Dashboard Endpoints page and locate an existing endpoint you'd like to add this to or create a new one.
- In your traffic policy, add the following configuration:
- YAML
- JSON
---
on_http_request:
- actions:
- type: oauth
config:
provider: microsoft
client_id: "{your app's oauth client id}"
client_secret: "{your app's oauth client secret}"
scopes:
- openid
- email
- profile
{
"on_http_request": [
{
"actions": [
{
"type": "oauth",
"config": {
"provider": "microsoft",
"client_id": "{your app's oauth client id}",
"client_secret": "{your app's oauth client secret}",
"scopes": [
"openid",
"email",
"profile"
]
}
}
]
}
]
}
- Click Save to validate and update your traffic policy.
Configure access control
Optionally, configure access control to your service by only allowing specific users or domains. For example:
- YAML
- JSON
# Only allow access to me@example.com. Add this after your OAuth Action.
---
on_http_request:
- expressions:
- "!(actions.ngrok.oauth.identity.email in ['me@example.com'])"
actions:
- type: deny
// Only allow access to me@example.com. Add this after your OAuth Action.
{
"on_http_request": [
{
"expressions": [
"!(actions.ngrok.oauth.identity.email in ['me@example.com'])"
],
"actions": [
{
"type": "deny"
}
]
}
]
}
Additional application setup information
- Creating an Azure AD tenant
- Permissions and consent (restricted permissions)
- Graph API User object properties (id, displayName, and mail/userPrincipalName)